投稿说明
| 投稿邮箱 | 内容说明 |
|---|---|
| ghostcp@outlook.com | 1. 注明投稿人昵称,并说明投稿练习题还是投稿解答; 2. 投稿的练习题应不过于复杂,参考答案100行以内为佳; 3. 如未注明昵称,投稿通过后将按照邮箱前缀在本文进行标注感谢; |
分类练习
文件及目录
- 练习一:实现与linux命令cp相同功能相同的程序,要求带有输入参数,第一个参数为源文件,第二个参数为目的文件。
答案:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
char *bTmp;
int fd_src, fd_desc;
int r_len;
if(argc < 3){
printf("arg num error!\n");
exit(1);
}
fd_src = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY, 0644);
if(fd_src == -1){
perror("open src");
exit(1);
}
fd_desc = open(argv[2], O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644);
if(fd_desc == -1){
perror("open desc");
exit(1);
}
bTmp = malloc(1024);
memset(bTmp, 0, 1024);
while((r_len = read(fd_src, bTmp, 1024)) > 0){
write(fd_desc, bTmp, r_len);
}
free(bTmp);
bTmp = NULL;
return 0;
}
- 练习二:实现与linux命令who相同功能的程序。
提示:在utmp.h中有一个结构体struct utmp,可保存登入用户的信息;文件/var/run/utmp中存放了所有用户的登入信息,其大小为n * sizeof(struct utmp)。实现的程序至少显示用户名及所登入的终端。
答案: 可以使用man 5 utmp查看struct utmp结构体中的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <utmp.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
char *src = "/var/run/utmp";
struct utmp *st_utmp;
int fd;
if((fd = open(src, O_RDONLY, 0644)) == -1){
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
st_utmp = malloc(sizeof(struct utmp));
memset(st_utmp, 0, sizeof(struct utmp));
while(read(fd, st_utmp, sizeof(struct utmp)) == sizeof(struct utmp)){
long t = st_utmp->ut_tv.tv_sec; //获取秒数
//非一般进程就跳过,详见百度百科“utmp”
if(st_utmp->ut_type != USER_PROCESS)
continue;
//user、line、time、host
printf("%s \t", st_utmp->ut_user);
printf("%s \t", st_utmp->ut_line);
printf("%.12s ", ctime(&t) + 4); //不显示"周"的4个字符开始显示12字符
printf("(%s)", st_utmp->ut_host);
printf("\n");
}
close(fd);
free(st_utmp);
st_utmp = NULL;
return 0;
}
- 练习三:使用link/symlink和unlink为一个文件添加和删除一个链接。
答案:link命令实现的是硬链接,symlink命令实现的是软链接(符号链接)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
if(((argc < 4) && (strcmp(argv[1], "link") == 0))
|| ((argc < 4) && (strcmp(argv[1], "symlink") == 0))
|| ((argc < 3) && (strcmp(argv[1], "unlink") == 0))){
printf("arg num error!\n");
exit(1);
}
if(strcmp(argv[1], "link") == 0){
if(link(argv[2], argv[3]) == -1){
perror("link");
}
}
else if(strcmp(argv[1], "symlink") == 0){
if(symlink(argv[2], argv[3]) == -1){
perror("symlink");
}
}
else if(strcmp(argv[1], "unlink") == 0){
if(unlink(argv[2]) == -1){
perror("unlink");
}
}
else{
printf("arg error!\n");
}
return 0;
}
- 练习四:目录扫描练习,实现与linux命令tree相同功能的程序。
答案:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <dirent.h>
static int s_grade = 0; //等级确定缩进
static int s_dirnum = 0, s_filenum = 0; //统计文件夹、文件数量
void DrawingLine(int grade){ //打印tree的一些树枝线条
int i;
if(grade == 0){
printf("├── ");
}
else{
printf("│");
for(i = 1; i < grade * 4; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("└── ");
}
}
void Tree(char *pbSrc){
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *entry;
if((dir_ptr = opendir(pbSrc)) == NULL){ //打开一个文件夹
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
entry = malloc(sizeof(struct dirent));
memset(entry, 0, sizeof(struct dirent));
while((entry = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL){ //逐条读取文件夹下的条目
if((strcmp(".", entry->d_name) == 0)
|| (strcmp("..", entry->d_name) == 0)){
continue;
}
DrawingLine(s_grade); //根据文件夹层数画线
if(entry->d_type == DT_DIR){
printf("%s/\n", entry->d_name);
s_dirnum++;
chdir(entry->d_name); //如果是文件夹就切换到该目录下
s_grade++; //增大等级
Tree("."); //递归调用
}
else{
printf("%s\n", entry->d_name);
s_filenum++;
}
}
chdir(".."); //目录扫描完成切换到上级目录
s_grade--; //减小等级
closedir(dir_ptr);
free(entry);
entry = NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
printf(".\n");
Tree(".");
printf("│\n%d directories, %d files\n", s_dirnum, s_filenum);
return 0;
}
- 练习五:文件属性练习,实现与linux命令
ls -l相同功能的程序。
答案:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <time.h>
/* 模式:d/-之类的 */
void mode(struct stat *p){
if(S_ISREG(p->st_mode))
putchar('-');
else if(S_ISDIR(p->st_mode))
putchar('d');
else if(S_ISCHR(p->st_mode))
putchar('c');
else if(S_ISBLK(p->st_mode))
putchar('b');
else if(S_ISFIFO(p->st_mode))
putchar('p');
else if(S_ISLNK(p->st_mode))
putchar('l');
else if(S_ISSOCK(p->st_mode))
putchar('s');
}
/* 用户权限 */
void usrm(struct stat *p)
{
if(p->st_mode & S_IRUSR)
putchar('r');
else
putchar('-');
if(p->st_mode & S_IWUSR)
putchar('w');
else
putchar('-');
if(p->st_mode & S_IXUSR)
putchar('x');
else
putchar('-');
}
/* 组权限 */
void grpm(struct stat *p)
{
if(p->st_mode & S_IRGRP)
putchar('r');
else
putchar('-');
if(p->st_mode & S_IWGRP)
putchar('w');
else
putchar('-');
if(p->st_mode & S_IXGRP)
putchar('x');
else
putchar('-');
}
/* 其他用户权限 */
void othm(struct stat *p)
{
if(p->st_mode & S_IROTH)
putchar('r');
else
putchar('-');
if(p->st_mode & S_IWOTH)
putchar('w');
else
putchar('-');
if(p->st_mode & S_IXOTH)
putchar('x');
else
putchar('-');
}
/* 所属用户名和组名 */
void name(struct stat *p)
{
struct passwd *passwd;
struct group *group;
passwd = getpwuid(p->st_uid);
group = getgrgid(p->st_gid);
printf("%s %s ", passwd->pw_name, group->gr_name);
}
void GetEntryStat(char *pbEntry){
struct stat *pst_stat = malloc(sizeof(struct stat));
memset(pst_stat, 0, sizeof(struct stat));
if(stat(pbEntry, pst_stat) == -1){
perror("stat");
exit(1);
}
mode(pst_stat); //文件模式d/-等
usrm(pst_stat); //用户权限
grpm(pst_stat); //组权限
othm(pst_stat); //其他用户权限
printf(" %ld ", pst_stat->st_nlink);//文件的硬链接数
name(pst_stat); //用户名和组名
printf("%ld \t", pst_stat->st_size);//文件大小
printf("%.12s ", ctime(&pst_stat->st_mtime)+4); //时间,只显示12字符
printf("%s\n", pbEntry); //文件(夹)名
free(pst_stat);
pst_stat = NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
char *cur_dir = "."; //当前文件夹
char *src_dir; //目标文件夹
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *entry;
if(argc > 1)
src_dir = argv[1];
else
src_dir = cur_dir;
if((dir_ptr = opendir(src_dir)) == NULL){
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
entry = malloc(sizeof(struct dirent));
memset(entry, 0, sizeof(struct dirent));
while((entry = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL){
if((strcmp(".", entry->d_name) == 0)
|| (strcmp("..", entry->d_name) == 0)){
continue;
}
chdir(src_dir);
GetEntryStat(entry->d_name);
}
free(entry);
entry = NULL;
return 0;
}
信号signal
- 练习:基于signal编写sleep功能函数
答案:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
void my_sig_hand(int sig_num){
//do nothing
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
struct sigaction new_sig, old_sig;
if(argc < 2){
printf("arg num error!\n");
exit(1);
}
//准备设置的结构体内容
new_sig.sa_handler = my_sig_hand;
sigemptyset(&new_sig.sa_mask);
sigaddset(&new_sig.sa_mask,SIGALRM);//将屏蔽SIGALRM加入到结构体
new_sig.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGALRM, &new_sig, &old_sig); //设置动作,并备份
alarm(atoi(argv[1])); //启动闹钟,超时会发SIGALRM到当前进程
sigdelset(&new_sig.sa_mask,SIGALRM);//将屏蔽SIGALRM从结构体去除
sigsuspend(&new_sig.sa_mask); //按照最新的屏蔽规则挂起
sigaction(SIGALRM, &old_sig, NULL); //还原默认动作
//以上操作主要是防止alarm定闹钟到挂起的时间里被高优先级进程打断
//从而闹钟失效后再进行挂起的风险
//故先屏蔽闹钟信号,挂起的同时撤销屏蔽
return 0;
}
进程
-
练习:实现一个简单的shell程序
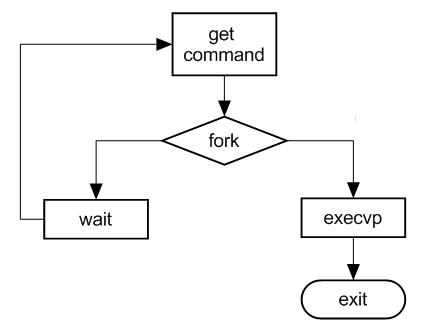
答案:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <wait.h>
void ShowTips(char *hostname){
char *wd = malloc(1024);
memset(wd, 0, 1024);
if((hostname != NULL) && (hostname != "")){
printf("%s:", hostname);
}
if(getcwd(wd, 1024) == NULL){
perror("getcwd");
exit(1);
//这里多说一点,现代操作系统都会自动回收内存
//手动free的好处是程序运行占用内存少,比如10M
//如果等程序结束自动释放,那么可能占用100M
//所以像exit命令前不用加free释放其他内存
}
printf("%s# ", wd);
free(wd);
wd = NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
char *bGetStr = malloc(2048);
static char *my_argv[32];
static int my_argc = 0;
memset(bGetStr, 0, 2048);
while(1){
ShowTips("");
//获取字符串并预处理
if(fgets(bGetStr, 2048, stdin) == NULL){
exit(1);
}
if(strlen(bGetStr) <= 1){
continue;
}
bGetStr[strlen(bGetStr) - 1] = '\0'; //替换最后的'\n'
//分段
my_argv[0] = strtok(bGetStr, " ");
while(my_argv[my_argc] != NULL){
my_argv[++my_argc] = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
//特殊处理exit和cd命令
if(strcmp(my_argv[0], "exit") == 0){
break;
}
else if(strcmp(my_argv[0], "cd") == 0){
if(my_argc >= 2){
if(chdir(my_argv[1]) == -1){
perror("chdir");
}
}
else{
if(chdir("/") == -1){
perror("chdir");
}
}
continue;
}
//其他命令统一开进程使用execvp进行替换程序
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0){
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
else if(id == 0){ //子进程
execvp(my_argv[0], my_argv);
exit(1);
}
else{ //父进程
int status = 0;
waitpid(id, &status, 0); //等待子进程
}
}
free(bGetStr);
bGetStr = NULL;
return 0;
}
套接字socket
- 练习一:编写面向有连接tcp程序
答案:
tcps.c 服务器端(多线程,支持多客户端)
目前是半双工(收到后被动发送),如果要支持全双工就给每个tcp连接建立两个线程,一个专门接收带被动发送,一个专门主动发送。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>//编译加 -pthread
#include <signal.h>
static const int port = 9999;
static const char *p = "0.0.0.0";
typedef struct Arg
{
int fd;
struct sockaddr_in addr;
}Arg;
void ProcessRequest(int new_sock, struct sockaddr_in *peer)
{
char buf[1024] = {0,};
printf("client %s:%d connect~\n", inet_ntoa(peer->sin_addr),\
ntohs(peer->sin_port));
while(1)
{
//读取
ssize_t s = read(new_sock, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1);
if(s > 0){
printf("[%s:%d] %s\n", inet_ntoa(peer->sin_addr),\
ntohs(peer->sin_port), buf);
if(strcmp(buf, "quit") == 0){
printf("client quit~\n");
break;
}
}
//写入
write(new_sock, buf, strlen(buf) + 1);
}
}
void *CreateWorker(void* ptr)
{
Arg* arg = (Arg*)ptr;
ProcessRequest(arg->fd, &arg->addr);
close(arg->fd);
free(arg);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int sfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); //创建socket
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(p); //sin_addr:4字节二进制
addr.sin_port = htons(port); //sin_port:2字节二进制
//上述结构体还会填充8字节0保持和struct sockaddr大小相同
//服务端(可选):设置端口重用(否则断开连接后等2~4分钟才可用)
int on = 1;
if(setsockopt(sfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &on, sizeof(on)) == -1){
perror("setsockopt");
exit(1);
}
//服务端:将地址和socket绑定
if((bind(sfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr))) == -1){
perror("bind");
exit(1);
}
//服务端:监听,这样其他进程才能连接
if((listen(sfd, 10)) == -1){
perror("listen");
exit(1);
}
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);//屏蔽tcp管道异常断开产生的信号(默认杀进程)
while(1){
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int new_sock = accept(sfd,(struct sockaddr *)&peer,&len);
if(new_sock == -1){
perror("accept");
exit(1);
}
pthread_t tid;
Arg *arg = (Arg *)malloc(sizeof(Arg));
arg->fd = new_sock;
arg->addr = peer;
//以下建立一个线程,要实现全双工请建立两个线程
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, CreateWorker, (void*)arg);
pthread_detach(tid);
}
return 0;
}
tcpc.c 客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
static const int port = 9999;
static const char *p = "0.0.0.0";
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int sfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); //创建socket,端口随机
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(p); //sin_addr:4字节二进制
addr.sin_port = htons(port); //sin_port:2字节二进制
//上述结构体还会填充8字节0保持和struct sockaddr大小相同
//客户端:根据远程addr进行连接
if((connect(sfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr))) == -1){
perror("connect");
exit(1);
}
while(1){
printf("mytcp>>> ");
char buf[1024] = {0,};
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, stdin); //输入字符,可以有空格
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0'; //替换回车为结束符
if(strlen(buf) > 0){
write(sfd, buf, strlen(buf) + 1); //发送用strlen
if(strcmp(buf, "quit")==0)
{
close(sfd);
exit(0);
}
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(sfd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1);//接收用sizeof
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
}
- 练习二:编写面向非连接udp程序
答案:
udps.c 服务器端(支持多客户端)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
static const int port = 10000;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int sfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
addr.sin_port = htons(port);
//服务端(可选):设置端口重用(否则断开连接后等2~4分钟才可用)
int on = 1;
if(setsockopt(sfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &on, sizeof(on)) == -1){
perror("setsockopt");
exit(1);
}
//服务端:将地址和socket绑定
if((bind(sfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr))) == -1){
perror("bind");
exit(1);
}
while(1){
char buf[1024] = {0,};
struct sockaddr_in peer = {0,};
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
recvfrom(sfd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1,0 , (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len);
if(strlen(buf) >0){
printf("[%s:%d] %s\n", inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr),\
ntohs(peer.sin_port), buf);
sendto(sfd, buf, strlen(buf) + 1,0 , (struct sockaddr *)&peer, len);
}
}
return 0;
}
udpc.c 客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
static const int port = 10000;
static const char *p = "0.0.0.0";
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int sfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(p);
addr.sin_port = htons(port);
while(1){
printf("myudp>>> ");
char buf[1024] = {0,};
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, stdin); //输入字符,可以有空格
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0'; //替换回车为结束符
if(strlen(buf) > 0){
sendto(sfd, buf, strlen(buf) + 1,0 , (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr));
if(strcmp(buf, "quit")==0)
{
close(sfd);
exit(0);
}
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
socklen_t len = sizeof(addr);
recvfrom(sfd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1,0 , (struct sockaddr *)&addr, &len);
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
}
收集练习
目前收集了如下地址的练习题:
| 百度文库1 | 百度文库2 |
题1~10
1、向文件f1中写入“hello world!”,然后再将f1中的内容读出并显示在屏幕上(注意必要的错误判断);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int fd;
char buf1[13] = "hello world!";
char buf2[12];
int num;
fd = open("f1", O_RDWD|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
if(fd == -1){
perror("f1 not open");
exit(1);
}
num = write(fd, buf1, sizeof(buf1) - 1);
if(num != sizeof(buf1) - 1){
printf("write less than want!\n");
}
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
num = read(fd, buf2, 12);
if(num != 12){
printf("read less than 12!\n");
}
write(1, buf2, 12);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
2、向文件f2中写入“aabbccddee”,然后将偏移量移到绝对值偏移为4的位置处,读6个字符,并将结果显示在屏幕上;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int fd;
char buf1[11] = "aabbccddee";
char buf2[10];
int num;
fd = open("f2", O_RDWD|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
if(fd == -1){
perror("f2 not open");
exit(1);
}
num = write(fd, buf1, sizeof(buf1) - 1);
if(num != sizeof(buf1) - 1){
printf("write less than want!\n");
}
lseek(fd, 4, SEEK_SET);
num = read(fd, buf2, 6);
if(num != 6){
printf("read less than 6!\n");
}
write(1, buf2, 6);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
3、向文件f3中写入“aabbccddeeffgghh”,然后将文件截短后的文件内容读出并显示在屏幕上;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int fd;
char buf1[17] = "aabbccddeeffgghh";
char buf2[8];
int num;
fd = open("f3", O_RDWD|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
if(fd == -1){
perror("f3 not open");
exit(1);
}
num = write(fd, buf1, sizeof(buf1) - 1);
if(num != sizeof(buf1) - 1){
printf("write less than want!\n");
}
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
ftruncate(fd, 8);
num = read(fd, buf2, 8);
if(num != 8){
printf("read less than 8!\n");
}
write(1, buf2, 8);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
4、在程序中将umask改至044,创建文件f4;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int fd;
umask(044);
creat("f4", S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR);
return 0;
}
5、实现“cat文件名”显示文件内容;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int fd;
int num;
char buf[10];
if(argc < 2){
printf("miss filename!\n");
exit(1);
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if(fd == -1){
perror("error open");
exit(1);
}
while((num = read(fd, buf, 10)) != 0){
write(1, buf, num);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
6、实现“cp原文件目标文件” ;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int from,to;
int num;
char buf[10];
if(argc < 3){
printf("argument error!\n");
exit(1);
}
from = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
to = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
num = read(from, buf, 10);
while(num != 0){
write(to, buf, num);
num = read(from, buf, 10);
}
close(from);
close(to);
return 0;
}
7、编写程序pro3.c,将字符串“hello world”通过输出重定向方式写入文件f1中;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int fd;
if((fd = open("f1", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 0644)) == -1){
perror("open fail");
exit(1);
}
if(dup2(fd, 1) == -1){
perror("redirect failed");
exit(1);
}
printf("Hello world!\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
}
8、使用fork创建进程,在子进程中打印”I am the child“和子进程pid,在父进程中打印“I am the father”和父进程pid;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
perror("fork");
}
else if(pid == 0){
printf("I am the child!pid is %d.\n", getpid());
}
else{
printf("I am the father!pid is %d.\n", getpid());
}
return 0;
}
9、创建子进程,在子进程中执行“ps -A”命令,父进程等待子进程结束后打印“child over” 及所处理的子进程进程号;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
pid_t pid, cpid;
int i;
char *args[64];
args[0] = "ps";
args[1] = "-A";
args[2] = NULL;
pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
perror("fork");
}
else if(pid == 0){
execvp(args[0], args);
exit(0);
}
else{
cpid = wait(NULL);
printf("child over! cpid=%d\n", cpid);
}
return 0;
}
10、编写程序处理SIGINT信号,当程序接收到SIGINT信号后输出“SIGINT is caught”;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
void signal_handler(int signum){
switch(signum){
case SIGINT:
printf("SIGINT is caught!\n");
break;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
signal(SIGINT, signal_handler);
pause();
return 0;
}
题11~20
11、使用PIPE时,限父子进程向子进程发送1234567890,子进程接收并显示;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int pfd[2];
char buf[32];
pid_t pid;
pipe(pfd);
if((pid = fork()) < 0){
perror("fork");
}
else if(pid > 0){
close(pfd[0]);
write(pfd[1], "1234567890", 11);
}
else{
close(pfd[1]);
read(pfd[0], buf, 11);
printf("child read:%s\n", buf);
}
return 0;
}
12、用多线程、信号量实现生产者和消费者的模拟,仓库容量为10,仓库中开始有3件产品,消费者每3秒消费一件产品,生产者每两秒生产一个产品,生产者和消费者不能同时进入仓库(需要互斥);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <phread.h>
#define msleep(x) usleep(x*1000)
#define PRODUCT_SPEED 3 //生产速度
#define COSTOM_SPEED 1 //消费速度
#define INIT_NUM 3 //仓库原有产品数
#define TOTAL_NUM 10//仓库容量
sem_t p_sem,c_sem,sh_sem;
int num = INIT_NUM;
void product(void){ //生产产品
sleep(PRODUCT_SPEED);
}
int add_to_lib(){ //添加产品到仓库
num++;
msleep(500);
return num;
}
void consum(){ //消费
sleep(CONSUM_SPEED);
}
int sub_from_lib(){ //从仓库中取产品
num--;
msleep(500);
return num;
}
void *productor(void *arg){
while(1){
sem_wait(&p_sem);//生产信号减一
product();//生产延时
sem_wait(&sh_sem);//用来互斥的信号
printf("push into!tatol_num=%d\n",add_to_lib());
sem_post(&sh_sem);
sem_post(&c_sem);//消费者信号量加一
}
}
void *consumer(void *arg){
while(1){
sem_wait(&c_sem);//消费者信号量减一
sem_wait(&sh_sem);
printf("pop out!tatol_num=%d\n",sub_from_lib());
sem_post(&sh_sem);
sem_post(&p_sem);//生产者信号量加一
consum();//消费延时
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
sem_init(&p_sem,0,TOTAL_NUM-INIT_NUM);
sem_init(&c_sem,0,INIT_NUM);
sem_init(&sh_sem,0,1);
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,productor,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,consumer,NULL);
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
13、编写一个多线程的程序
要求:
1、创建2个子线程,主线程要传递3个参数给线程1,传递另一个参数给线程2;
2、线程1、线程2对每个传给线程的参数加1,等线程都执行完毕后,进程打印出四个参数的值;
3、传给线程1参数的值必须要能够改变,传给线程2参数的值必须不能改变;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
typedef struct{
int A;
int B;
int C;
}DATA;
/*传参方法1*/
void *thread_1(void *arg){
DATA *rec;
sleep(1);
rec = (DATA *)arg;
rec->A += 1;
rec->B += 1;
rec->C += 1;
return NULL;
}
/*传参方法2*/
void *thread_2(void *arg){
int rec = 0;
sleep(1);
rec = (int)arg;
rec++;
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
DATA test;
int D = 100;
test.A = 100;
test.B = 100;
test.C = 100;
/*创建两个线程*/
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, (void *)thread_1, (void *)(&test));
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, (void *)thread_2, (void *)D);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
printf("A=%d\n", test.A);
printf("B=%d\n", test.B);
printf("C=%d\n", test.C);
printf("D=%d\n", D);
return 0;
}
14、编制一段程序,实现进程的管道通信
使用系统调用pipe()建立一条管道线,2个子进程分别向管道各写一句话:
Child process 1 is sending a message!
Child process 2 is sending a message!
要求:父进程先接收子进程P1发来的消息,然后再接收子进程P2发来的消息;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
pid_t pid_sec;
char buf[7];
pipe(fd);
if((pid = fork()) < 0){
perror("fork error");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid == 0){
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1], "first1", 7);
close(fd[1]);
exit(0);
}
else{
if((pid_sec = fork()) < 0){
perror("fork second error");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid_sec == 0){
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1], "Child1", 7);
close(fd[1]);
exit(0);
}
else{
wait(0);
close(fd[1]);
read(fd[0], buf, 7);
printf("%s\n", buf);
wait(0);
close(fd[1]);
read(fd[0], buf, 7);
close(fd[0]);
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
}